Edible Landscapes: Merging Luxury with Functionality
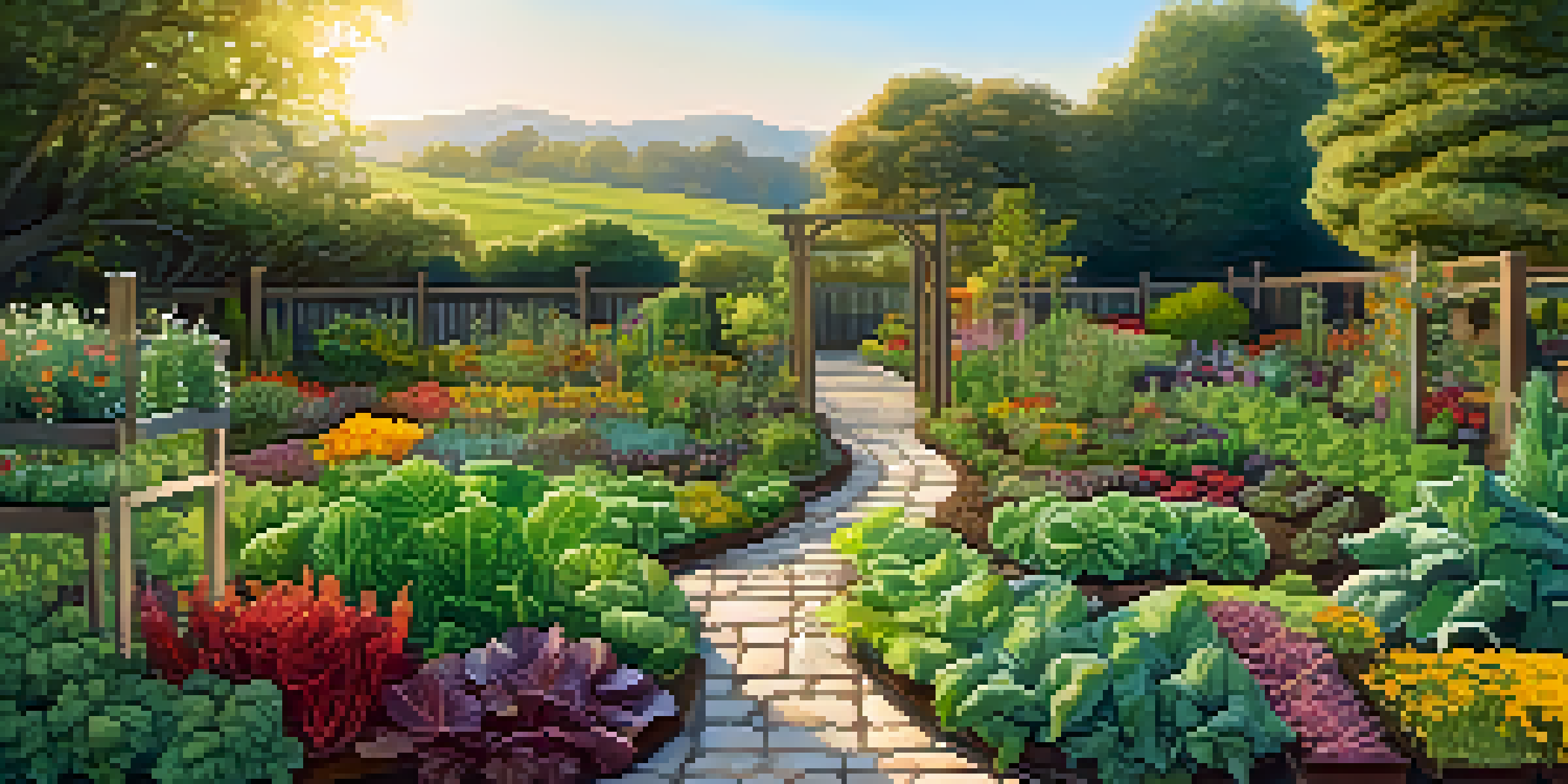

What Are Edible Landscapes and Why They Matter
Edible landscapes are gardens designed to incorporate food-producing plants into the overall aesthetic. Imagine strolling through a beautifully arranged garden, only to find that the vibrant flowers are also herbs and vegetables. This approach not only enhances the beauty of outdoor spaces but also promotes sustainability and self-sufficiency.
To plant a garden is to believe in tomorrow.
With an increasing focus on local food production and environmental wellness, edible landscapes offer a practical solution. They allow homeowners to grow their own food, turning backyards into bountiful gardens while reducing reliance on store-bought produce. This transformation encourages a deeper connection to nature and a healthier lifestyle.
Moreover, edible landscapes can elevate the overall design of a property. They seamlessly blend luxury with functionality, making outdoor spaces inviting while serving a purpose. By integrating fruits, vegetables, and herbs into landscaping, homeowners can create unique and visually appealing environments that stand out.
The Aesthetic Appeal of Edible Plants
One of the most striking features of edible landscapes is their aesthetic appeal. Plants like kale, Swiss chard, and even berry bushes contribute vibrant colors and textures that beautify any garden. When designed thoughtfully, these edible plants can serve as focal points, much like ornamental flowers.

For instance, a trellis adorned with climbing beans can create a stunning visual while providing nutritious produce. The key is to select plants that not only taste good but also look great in the landscape. By doing so, homeowners can enjoy the visual charm of their gardens while also reaping the benefits of fresh food.
Edible Landscapes Enhance Aesthetics
Integrating food-producing plants into gardens not only beautifies outdoor spaces but also promotes sustainability.
Additionally, edible plants can attract beneficial wildlife, such as pollinators and birds, enhancing the overall ecosystem. This connection to nature not only enriches the garden's beauty but also supports biodiversity, making the space more vibrant and alive.
Design Principles for Edible Landscapes
Creating an edible landscape involves thoughtful design principles that marry beauty and utility. Start by considering the layout—mixing edible plants with ornamental ones can create a harmonious blend. Grouping plants by height and color can also enhance visual interest, leading to an eye-catching garden.
The greatest fine art of the future will be the making of a comfortable living from a small piece of land.
Another essential principle is seasonality. Choosing a variety of plants that thrive at different times of the year ensures that the garden remains productive and attractive throughout the seasons. This approach not only maximizes yield but also keeps the garden visually dynamic as it changes with the seasons.
Finally, integrating pathways and seating areas can transform your garden into a functional outdoor living space. A well-designed edible landscape invites you to explore, relax, and enjoy the fruits of your labor, making it a luxurious retreat for both the senses and the palate.
Sustainability Benefits of Edible Landscapes
Edible landscapes play a significant role in promoting sustainability. By growing food at home, individuals can reduce their carbon footprint associated with transportation and packaging of store-bought produce. This shift towards local food production not only benefits the environment but also encourages a healthier diet.
Moreover, incorporating native plants into the garden can help conserve water and support local ecosystems. Native species are adapted to local conditions and often require less maintenance, making them a sustainable choice for any edible landscape. This thoughtful selection can lead to a garden that thrives with minimal intervention.
Sustainability Through Local Production
Growing food at home reduces carbon footprints and fosters a culture of environmental stewardship.
Additionally, edible landscapes can serve as vital educational tools for communities. They inspire individuals to learn about food systems, gardening, and the importance of sustainable practices, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
Choosing the Right Edible Plants
Selecting the right edible plants is crucial for creating a successful edible landscape. Factors such as climate, soil type, and personal taste should guide your choices. Start with plants that are well-suited to your local environment, as they will be more resilient and easier to grow.
Consider incorporating a mix of annuals and perennials to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the year. For example, herbs like basil and cilantro can be replanted each year, while fruit-bearing plants like strawberries and blueberries can provide yields for many seasons. This combination not only maximizes productivity but also enhances the garden's diversity.
Don't forget to include plants that can be both ornamental and edible, such as nasturtiums or edible flowers. These choices add color and flair to the landscape while contributing to the overall functionality of the garden.
Maintenance Tips for Edible Landscapes
Maintaining an edible landscape can be straightforward with the right approach. Regular watering, especially during dry spells, is essential for the health of your plants. Consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water efficiently and conserve resources.
Weeding is another critical maintenance task that helps your plants thrive. Keeping the area free from competition ensures that your edible plants get the nutrients they need. Mulching can help suppress weeds while retaining moisture, making it a valuable addition to your maintenance routine.
Smart Plant Choices are Key
Selecting the right mix of edible plants based on climate and personal taste ensures a thriving garden.
Lastly, be mindful of pests and diseases. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of trouble and take preventive measures, such as introducing beneficial insects or using organic pest control methods. This proactive approach not only protects your investment but also promotes a healthier garden ecosystem.
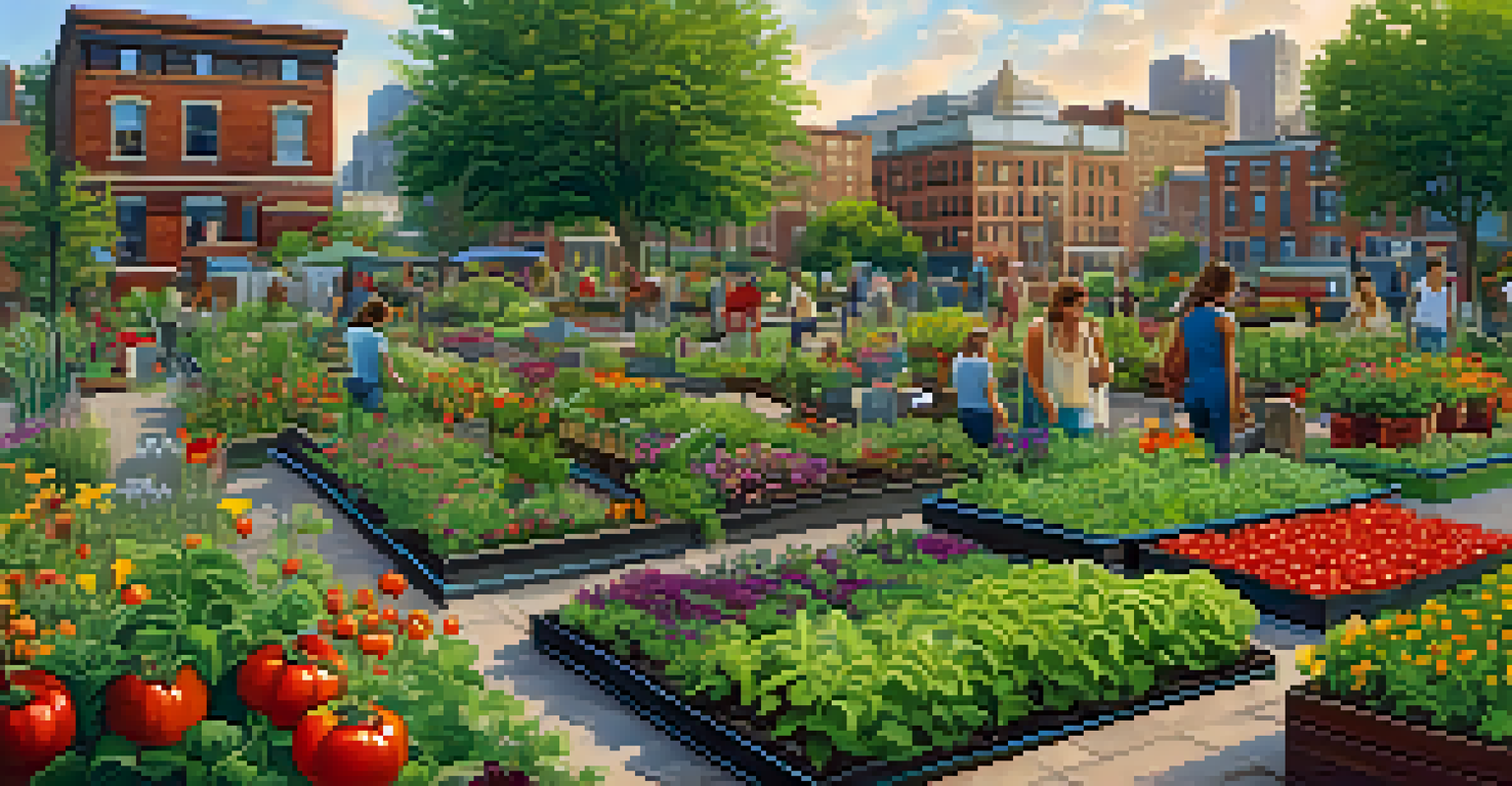
Inspiration from Successful Edible Landscapes
Looking at successful edible landscapes can provide inspiration for your own garden. Many urban areas now showcase community gardens that blend aesthetics with functionality, proving that beauty and practicality can coexist. For example, the Edible Schoolyard Project in Berkeley, California, has transformed schoolyards into lush gardens where students learn about food and sustainability.
Additionally, many homeowners are embracing the trend of front-yard vegetable gardens, challenging traditional landscaping norms. These edible front yards not only beautify neighborhoods but also encourage community involvement and sharing of resources. Imagine walking down your street and spotting a colorful array of tomatoes, peppers, and herbs instead of just ornamental shrubs.
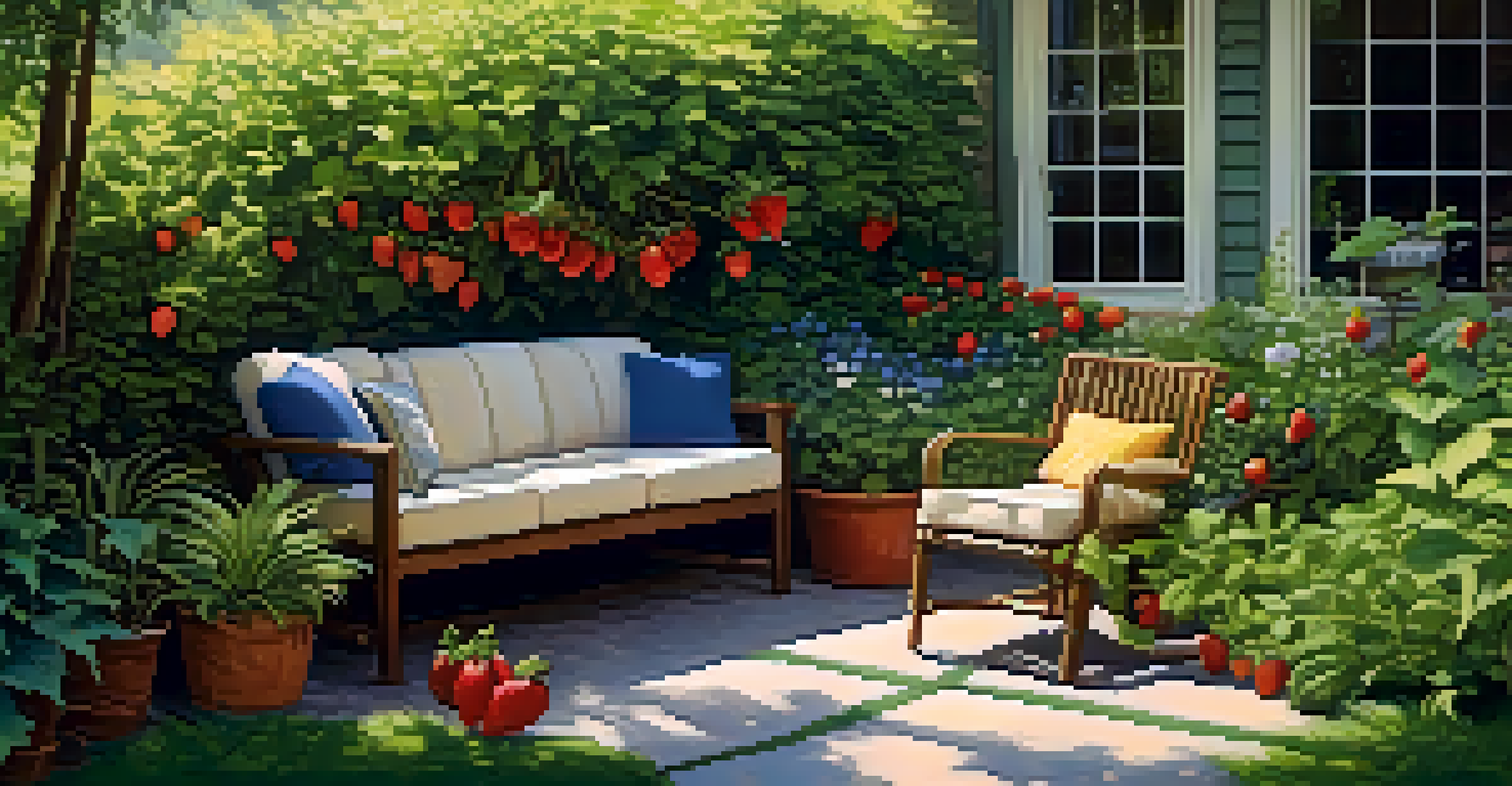
These real-life examples demonstrate that edible landscapes can be both luxurious and practical, inspiring others to rethink their own outdoor spaces. By sharing stories of successful gardens, we can cultivate a broader movement toward integrating food production into everyday life.